In the daily operations of any organization, unexpected events like accidents or near-misses can occur. To formally document these incidents and ensure transparency and safety, incident reporting plays a crucial role.
Incident reports are used to investigate causes, implement corrective actions, prevent future occurrences, ensure regulatory compliance, and maintain overall safety within an organization. These reports serve as official records for learning, risk identification, and demonstrating a commitment to a safe environment.
What is Incident Reporting?
Incident reporting is the process of documenting unexpected events that occur within an organization. This documentation is essential for understanding the root causes of incidents, implementing corrective actions, and preventing similar incidents from happening in the future.
By reporting incidents, organizations can maintain transparency, ensure compliance with regulations, and promote a culture of safety. Incident reports provide a detailed account of what happened, why it happened, and what steps need to be taken to prevent it from happening again.
The Importance of Incident Reporting
Incident reporting is crucial for organizations to identify potential risks, improve safety measures, and prevent future incidents. By documenting incidents, organizations can analyze trends, identify patterns, and implement corrective actions to mitigate risks. Incident reports also help organizations demonstrate their commitment to safety and compliance with regulations. Additionally, incident reporting fosters a culture of transparency and accountability within an organization, encouraging employees to report incidents without fear of reprisal.
Promotes Safety and Prevents Future Incidents
Effective incident reporting helps organizations identify hazards, assess risks, and implement preventive measures to ensure the safety of employees, customers, and stakeholders. By reporting incidents promptly and accurately, organizations can prevent similar incidents from occurring in the future and create a safer work environment for all.
Ensures Compliance with Regulations
Compliance with regulations is a critical aspect of incident reporting. By documenting and reporting incidents in accordance with regulatory requirements, organizations can avoid penalties, fines, or legal consequences. Incident reports serve as a record of compliance with health and safety regulations, environmental standards, and other industry-specific requirements.
Facilitates Continuous Improvement
Incident reporting is not just about documenting incidents; it’s also about learning from them. By analyzing incident reports, organizations can identify areas for improvement, implement corrective actions, and enhance operational efficiency. Continuous improvement based on incident data allows organizations to proactively address risks, prevent future incidents, and create a safer workplace for everyone.
Enhances Risk Management
Risk management is an essential component of incident reporting. By identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks through incident reporting, organizations can minimize the likelihood of accidents, injuries, and financial losses. Incident reports provide valuable data that can inform risk management strategies, improve safety protocols, and protect the organization from potential liabilities.
Builds Trust and Transparency
Encouraging incident reporting builds trust among employees, customers, and stakeholders. When organizations prioritize safety and transparency through incident reporting, they demonstrate a commitment to the well-being of their workforce and the community. Trust and transparency foster a positive organizational culture where employees feel valued, heard, and supported in maintaining a safe work environment.
Supports Decision-Making
Incident reports provide valuable insights that can inform decision-making processes within an organization. By analyzing incident data, organizations can identify trends, prioritize safety initiatives, and allocate resources effectively. Incident reports serve as a basis for informed decision-making, helping organizations proactively address risks, improve processes, and enhance overall safety performance.
Demonstrates Organizational Commitment
Prioritizing incident reporting demonstrates an organization’s commitment to safety and well-being. When organizations invest in incident reporting processes, implement corrective actions, and prevent future incidents, they showcase a dedication to maintaining a safe and secure work environment. This commitment not only protects employees and stakeholders but also enhances the organization’s reputation as a responsible and conscientious entity.
Encourages Employee Engagement
Creating a culture that values incident reporting encourages employees to actively participate in safety initiatives. When employees feel empowered to report incidents, voice concerns, and contribute to a safer work environment, they become more engaged in promoting safety and well-being. Employee engagement in incident reporting fosters a sense of ownership, responsibility, and collaboration in maintaining a culture of safety within the organization.
Types of Incidents That Should Be Reported
Incident reporting is not limited to just accidents or injuries; it encompasses a wide range of unexpected events that can impact the safety and well-being of individuals within an organization. Some common types of incidents that should be reported include:
Accidents
Accidents are unexpected events that result in injury, damage, or loss. Whether it’s a slip-and-fall accident, a machinery malfunction, or a vehicle collision, accidents should be promptly documented and reported to prevent similar incidents in the future. Accurate reporting of accidents allows organizations to investigate causes, implement corrective actions, and improve safety protocols.
Near-Misses
Near-misses are incidents that could have resulted in harm but were narrowly avoided. While no injuries or damages may have occurred, near-misses are valuable indicators of potential hazards and risks within an organization. Reporting near-misses helps organizations identify areas for improvement, implement preventive measures, and create a safer work environment for all.
Workplace Violence
Workplace violence encompasses any act or threat of physical violence, harassment, or intimidation in the workplace. Incidents of workplace violence should be reported promptly to ensure the safety and well-being of employees. By documenting and addressing instances of workplace violence, organizations can create a zero-tolerance policy, provide support to affected individuals, and prevent future incidents from occurring.
Property Damage
Property damage refers to any damage to equipment, facilities, or property within the organization. Whether it’s a fire, a flood, or vandalism, incidents of property damage should be reported to assess the extent of the damage, determine the causes, and implement measures to prevent future occurrences. Timely reporting of property damage helps organizations safeguard their assets and maintain a secure work environment.
Environmental Incidents
Environmental incidents include spills, leaks, or other incidents that impact the environment. Whether it’s a chemical spill, a waste disposal issue, or pollution, environmental incidents should be reported to prevent further damage to the environment and comply with environmental regulations. Reporting environmental incidents allows organizations to take corrective actions, minimize environmental impact, and demonstrate their commitment to environmental stewardship.
Security Breaches
Security breaches involve unauthorized access, theft, or breach of security protocols within an organization. Whether it’s a data breach, a cybersecurity attack, or a physical breach of security, incidents of security breaches should be reported promptly to protect sensitive information, prevent further breaches, and enhance security measures. Reporting security breaches helps organizations safeguard their assets, reputation, and integrity.
Health and Safety Violations
Health and safety violations refer to breaches of health and safety regulations or protocols within the organization. Whether it’s a failure to provide personal protective equipment, inadequate training on safety procedures, or violations of safety standards, incidents of health and safety violations should be reported to ensure compliance and prevent injuries or illnesses. Reporting health and safety violations helps organizations maintain a safe work environment, protect employees’ well-being, and comply with regulatory requirements.
What to Include in a Good Incident Report
When preparing an incident report, it is essential to include specific details that provide a comprehensive understanding of the incident. A good incident report should include the following elements:
Date, Time, and Location of the Incident
Including the date, time, and location of the incident provides essential context for understanding when and where the incident occurred. This information helps establish a timeline of events and can aid in the investigation process to determine the causes and contributing factors of the incident.
Description of What Happened
A detailed description of what happened during the incident is crucial for capturing the sequence of events, actions taken, and outcomes. Providing a thorough account of the incident helps stakeholders understand the nature of the event, its impact, and the potential risks involved. The description should be objective, factual, and free from personal opinions or biases to ensure accuracy and clarity in reporting.
Factors Contributing to the Incident
Identifying the factors that contributed to the incident is essential for determining the root causes and underlying issues that led to the event. This may include human factors, environmental conditions, equipment malfunctions, communication breakdowns, or other variables that played a role in the incident. By analyzing these contributing factors, organizations can implement targeted corrective actions to prevent similar incidents in the future.
Witness Statements or Accounts
Collecting witness statements or accounts from individuals who were present during the incident provides valuable perspectives and additional insights into what transpired. Witness statements can corroborate details, verify information, and fill in gaps in the incident report. Including witness accounts helps create a comprehensive and accurate record of the incident, enhancing the investigation process and decision-making regarding preventive measures.
Injuries or Damages Incurred
Documenting any injuries, damages, or losses incurred as a result of the incident is critical for assessing the impact and severity of the event. Whether it’s physical injuries to individuals, property damage, financial losses, or reputational harm, recording the extent of the consequences helps organizations understand the implications of the incident and prioritize response actions accordingly.
Actions Taken Immediately Following the Incident
Detailing the actions taken immediately following the incident is essential for documenting response efforts, mitigating risks, and ensuring the safety of individuals involved. This may include emergency response measures, medical treatment for injuries, containment of hazards, notification of authorities, or evacuation procedures. By documenting the immediate actions taken, organizations can assess the effectiveness of their response protocols and identify areas for improvement.
Recommendations for Preventing Future Incidents
Including recommendations for preventing future incidents is a proactive approach to incident reporting that focuses on risk mitigation and continuous improvement. Based on the findings of the incident investigation, organizations can develop specific recommendations for corrective actions, safety measures, training programs, or policy changes. These recommendations aim to address root causes, eliminate hazards, and enhance safety practices to prevent similar incidents from occurring in the future.
Signatures of Individuals Involved in the Incident Report
Obtaining signatures of individuals involved in the incident report, such as witnesses, supervisors, or affected parties, adds credibility and accountability to the document. Signatures indicate acknowledgment and agreement with the information presented in the report, confirming the accuracy of the details provided. By capturing signatures, organizations ensure that all relevant stakeholders are aware of the incident and committed to implementing recommended actions for prevention.
How to Write an Effective Incident Report
Writing an effective incident report requires attention to detail, clarity, and objectivity. When documenting an incident, follow these guidelines to ensure your report is accurate and informative:
Begin by Stating the Facts Clearly
Start your incident report by stating the facts of the incident clearly and concisely. Provide essential details such as the date, time, location, and individuals involved to establish the context of the event. Avoid embellishments or assumptions and focus on presenting the information objectively.
Provide a Chronological Account of Events
Present a chronological account of events leading up to the incident to create a timeline of how the incident unfolded. Describe the sequence of actions, interactions, and circumstances that occurred before, during, and after the incident. A chronological narrative helps readers understand the progression of events and identify potential triggers or contributing factors.
Include Relevant Details and Information
Include relevant details and information that are essential for understanding the incident. This may include descriptions of the surroundings, equipment involved, procedures followed, and any other pertinent factors that influenced the outcome. Providing specific details enhances the accuracy and completeness of the report, enabling a more thorough analysis of the incident.
Avoid Speculation or Assumptions
Maintain objectivity in your incident report by avoiding speculation, assumptions, or personal opinions. Stick to the facts and observations based on firsthand accounts, evidence, and documentation. Speculative language can introduce bias and inaccuracies into the report, potentially affecting the validity of the findings and recommendations.
Use Clear and Objective Language
Communicate the details of the incident using clear, objective language that is easy to understand. Avoid technical jargon or ambiguous terms that may confuse readers or obscure the meaning of the report. Use simple and direct language to convey information accurately and concisely, maintaining a professional tone throughout the document.
Include Supporting Documentation
If available, include supporting documentation such as photos, diagrams, witness statements, or incident records to provide additional context and evidence. Visual aids and supplementary materials can enhance the clarity and credibility of the report by providing visual representations of the incident scene, injuries, damages, or other relevant information. Ensure that all supporting documentation is accurate, relevant, and properly referenced in the report.
Conclude with Recommendations for Prevention
Conclude the incident report with recommendations for preventing similar incidents in the future. Based on the analysis of the incident, identify specific actions, controls, or measures that can be implemented to reduce risks, enhance safety practices, or improve procedures. Clearly outline the preventive measures and their expected outcomes to guide decision-making and promote proactive risk management within the organization.
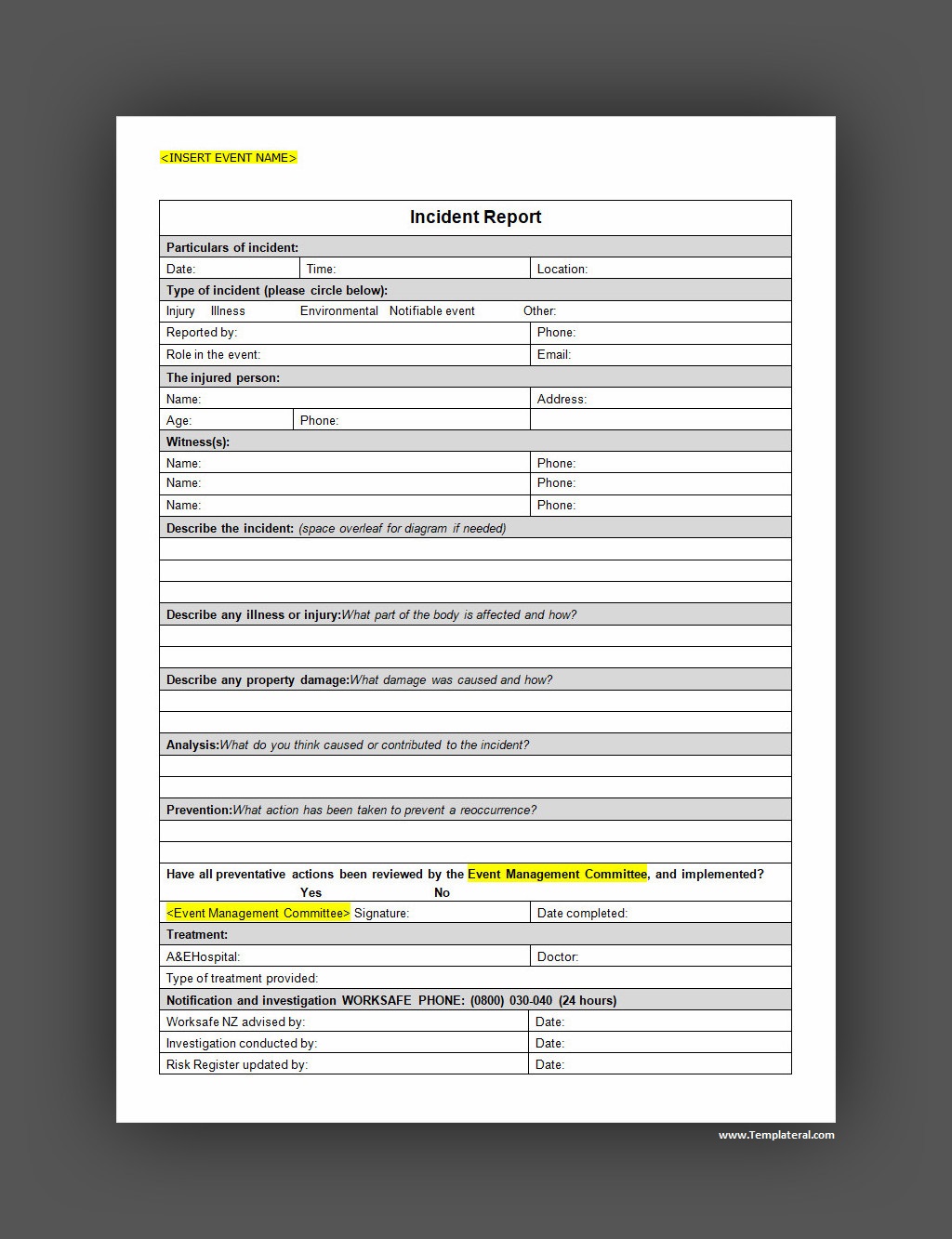
Incident Report Template
An incident report is a practical tool for documenting accidents, injuries, or unexpected events in a clear and organized manner. It helps ensure accurate records, improves accountability, and supports follow-up actions.
To make reporting simple and effective, use our free incident report template and keep all details properly documented.
Incident Report Template – Word