Bank statements are a vital financial document that provides a formal record of all transactions in a bank account over a specific period. They play a crucial role in helping account holders track their finances, detect errors or fraud, monitor spending habits, reconcile their accounts, and serve as proof of financial activity for tasks like applying for loans or filing taxes.
In this article, we will delve into the specifics of bank statements, their purpose, how they work, the benefits they offer, the different types available, and the components that make up a bank statement.
What is a Bank Statement?
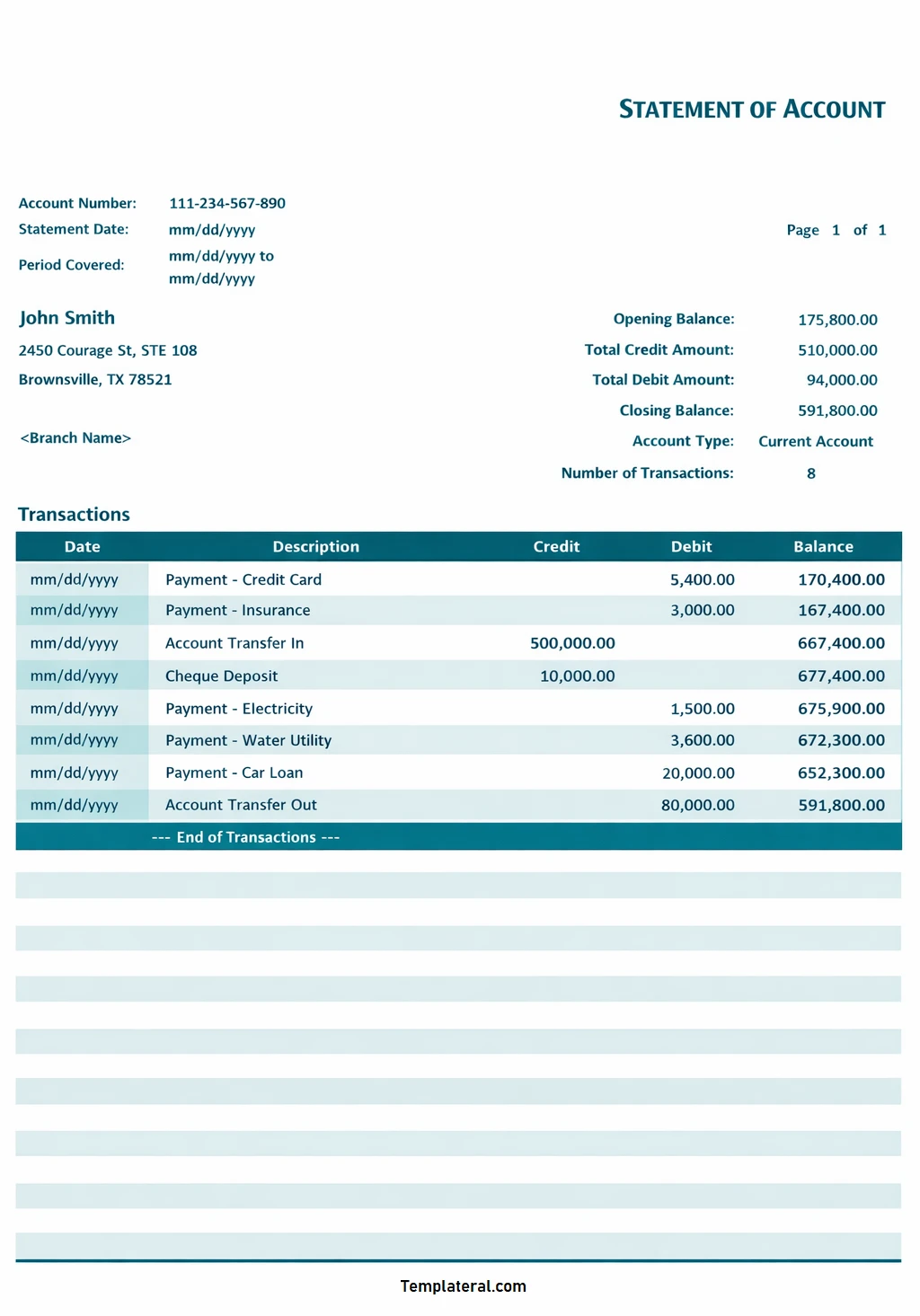
A bank statement is essentially a summary of all the transactions that have occurred in a specific bank account over a set period of time, typically monthly. It includes details such as deposits, withdrawals, transfers, fees, and interest earned.
This document serves as a crucial tool for account holders to keep track of their financial activities and maintain an accurate record of their banking transactions.
What is the Purpose of a Bank Statement?
The primary purpose of a bank statement is to provide a detailed account of all the financial transactions that have taken place in a particular bank account. This information allows account holders to monitor their spending, detect any unauthorized or incorrect charges, reconcile their accounts with their own records, and plan for future financial decisions.
Additionally, bank statements serve as proof of income and expenses for various purposes, such as applying for loans or mortgages, filing taxes, or resolving disputes with merchants.
How a Bank Statement Works
Bank statements are typically generated by financial institutions at the end of each monthly cycle. Account holders can access their bank statements through online banking portals or receive physical copies in the mail.
The statement will include a summary of all transactions, starting and ending balances, any fees charged, and interest earned. Account holders should review their bank statements regularly to ensure the accuracy of the information and report any discrepancies to their bank promptly.
Benefits of a Bank Statement
Bank statements offer a range of benefits to account holders, including:
- Financial Tracking. Account holders can track their income and expenses to better manage their finances.
- Error Detection. Bank statements help identify any unauthorized or incorrect charges that may have occurred.
- Budgeting. By reviewing their bank statements, account holders can create budgets and savings goals.
- Proof of Income. Bank statements serve as proof of income when applying for loans or mortgages.
- Financial Planning. Account holders can use bank statements to plan for future expenses and investments.
Different Types of Bank Statements
There are several types of bank statements available to account holders, depending on their banking preferences and needs. Some common types include:
1. Paper Statements
Paper statements are physical copies of bank statements that are mailed to account holders monthly. They provide a tangible record of financial transactions that can be stored for future reference.
2. Electronic Statements
Electronic statements, also known as e-statements, are digital versions of bank statements that can be accessed through online banking portals. They offer a convenient and eco-friendly way to view and manage financial transactions.
3. Consolidated Statements
Consolidated statements combine multiple accounts or products into a single statement for easy tracking and management. This can include checking, savings, and investment accounts on one comprehensive statement.
4. Credit Card Statements
Credit card statements provide a summary of all charges, payments, and fees associated with a credit card account. They help account holders monitor their credit card usage and track their spending habits.
5. Mortgage Statements
Mortgage statements detail the payments, interest, and remaining balance on a mortgage loan. They help homeowners keep track of their mortgage payments and progress towards owning their home outright.
Components of a Bank Statement
A typical bank statement will include the following components:
- Account Information. This section includes details such as the account holder’s name, account number, and contact information.
- Transaction History. A detailed list of all transactions, including deposits, withdrawals, transfers, fees, and interest earned.
- Starting and Ending Balances. The beginning and ending balances for the statement period show the overall financial activity in the account.
- Fees and Charges. Any fees or charges assessed by the bank, such as overdraft fees or service charges.
- Interest Earned. Details on any interest earned on the account balance during the statement period.
Overall, bank statements are an essential tool for managing personal finances and keeping track of financial activities. By understanding how bank statements work, their purpose, and the benefits they offer, account holders can make informed decisions about their money and ensure their financial well-being.
Bank Statement Template – DOWNLOAD